HUMANIPA platform for development of intelligent conversational agents (AI-based CA)
The functional architecture of the HUMANIPA platform. The hardware platform for HUMANIPA cognitive platform is being built as part of an internal project DSPLab IoT
(1) Linguistic expressions should be linked to non-linguistic, especially perceptual (information that is a source of modality such as vision, acoustics, etc.), as this is essentially a key aspect for gaining meaning and understanding of conversational acts. This is a longstanding challenge for artificial intelligence. In this context we focus, in the presented system architecture, on using multimodal information to understand, learn, and generate conversational behavior on intelligent conversational agents.
(2) We build data resources (EVA-Corpus) and set the standard for a multimodal data source that will allow a more complete description of the conversational behavior that characterize spontaneous human-human interactions. In this part of the system, research is being carried out in the fields of multimodal (E)CA and CI, multimodal linguistics, and multimodal social dialogue systems, through consolidation and use of various multimodal corpora (e.g. Nomco corpus), covering the information needed to address the research questions, tasks, and hypotheses defined within the Humanipa project. Project activity is also strongly linked in this regard to the project COST CA18231
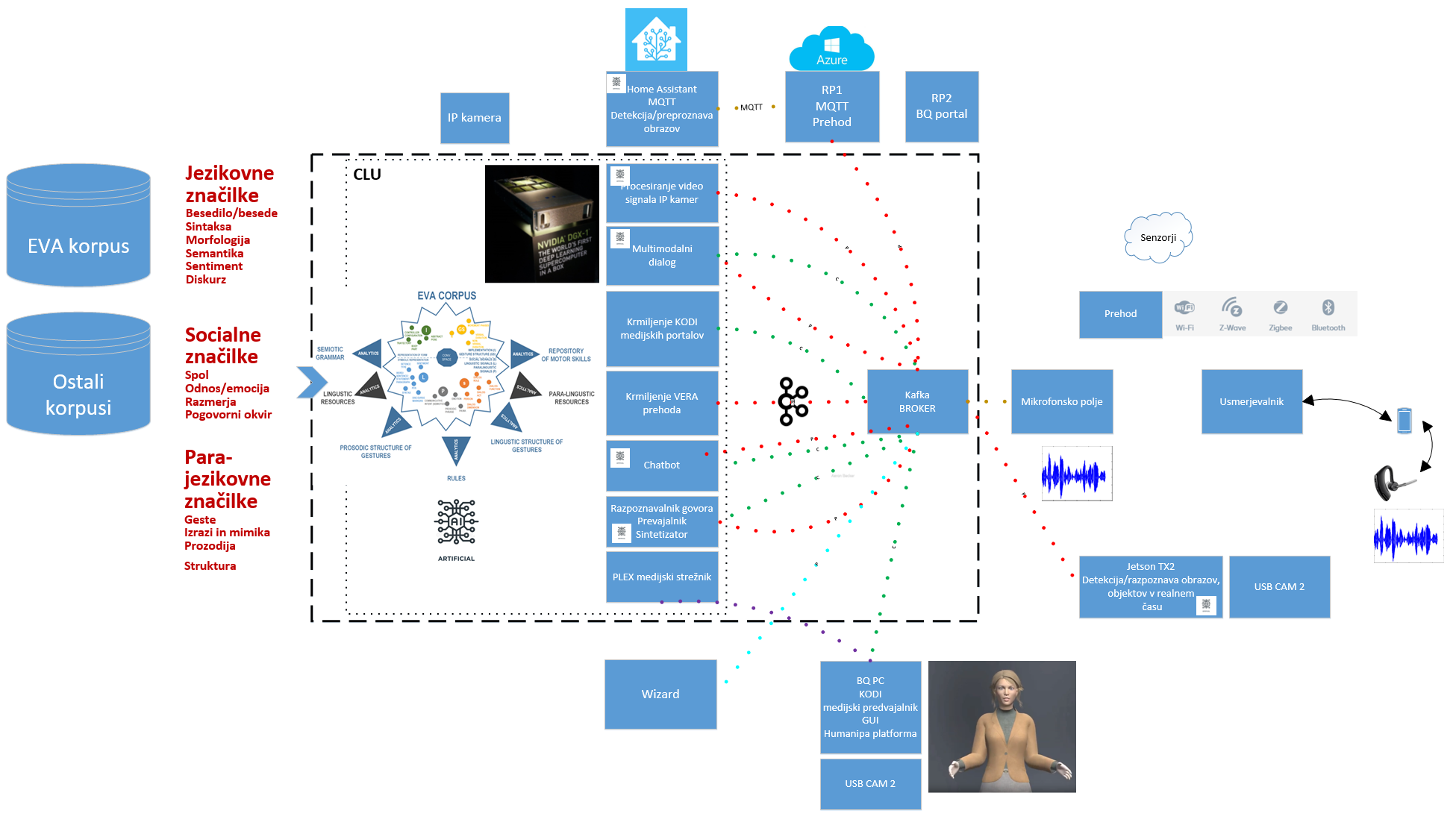
(3) In the scope of the project, we are developing a new CLU concept as a unique approach that develops the idea that verbal and nonverbal conversational signals are complementary, and equally important in conversational expressions. We are developing a new fusion-based model, as well as AI-based algorithms that will be able to generate in-depth understanding in cognitive interplay for communicative intent as a central core of the human-human spontaneous interaction. These algorithms are based on deep learning techniques, and use signals contained in the EVA-Corpus. In addition to the field of natural language processing (NLP), and understanding of spoken language (NLU), are considered as an important role in human-machine interaction also gestures and all non-verbal communication as well as expression of information not only through words. In direct spontaneous interaction, are non-verbal signals generated and transmitted together with the spoken content (or even in the absence thereof), and are therefore crucial for establishing cohesion in a discourse. The verbal/linguistic parts of the spoken language (e.g. words, grammar, syntax) carry a symbolic/semantic interpretation of the message, while the co-verbal parts (e.g. gestures, expressions, prosody) carry the social component of each message, and serve as the orchestrator of all the communication, we want to present and understand it appropriately within the CLU. Thus, in the architecture, the CLU represents a fusion model based on a multi-channel/multi-signal representation of an idea using audio and visual signals; e.g. as a global fusion function consisting of several partial functions that process individual groups of signals in the conversational space.
(4-6) Within the CLU, we develop effective machine learning algorithms, methods, and applications to generate conversational behavior. We are interested in ML techniques that stand for state-of-the-art language generation (LG) models, which have made significant progress at the expense of the use of different deep neural network architectures, and multimodal data integration strategies. Thus, within CLU we develope software for language and visual content processing. The system architecture incorporates deep learning solutions as part of this module, namely machine translation of text/ transcriptions, continuous speech recognition, speech synthesis, and chatbot systems, such as: Chatterbot and Rasa. CLU is being developed for multiple languages according to the project requirements in PERSIST.
(7) All processing and data flow (speech, text, sensor data, visual data, etc.) are integrated by using the Apache Kafka system. Kafka is used to develop real-time data pipelining and streaming applications. It is horizontally scalable, and fault tolerant.